This is a sister article to "Setting up a Home Network DSL/Router" and it discusses basic network trouble-shooting and diagnostic techniques.
This article can help you determine which component on has failed and it assumes a network wired in this fashion, with these example IP Addresses. Your addresses may be different:
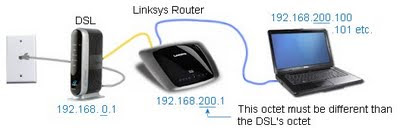 If your home network intermittently "crashes" (especially when a laptop is booted and first logs in), see this very interesting article: Windows 7 and Vista Network Problems (IPV6)
If your home network intermittently "crashes" (especially when a laptop is booted and first logs in), see this very interesting article: Windows 7 and Vista Network Problems (IPV6)Ideally, you would have recorded your previous network configuration by simply making a drawing like the illustration above -- but most people do not bother and this makes diagnostics more difficult.
Assuming you have previously configured your DSL Modem and Router, but you are still having connection problems. Consider these tests. You will need to test both the Linksys Router and the DSL modem. Similar steps work for Cable and non-Linksys routers.
Confirm the Workstation
1. From any workstation, open a DOS Prompt by clicking Start, All Programs, Accessories, "Command Prompt"
or optionally, Start, Run, "cmd" (enter) See this article: Exposing the Run command.
2. Confirm the current workstation has an IP Address with this DOS command:
ipconfig
Look for an IPV4 address similar to: 192.168.200.100 (or 101, etc.).
This is an address from the Linksys router's DHCP pool.
3. If IPConfig reports no IP Address (0.0.0.0 -- Address not found):
Confirm the network cable is plugged in or if a wireless, confirm the wireless card is active. If you have a laptop, it is easiest to test the network with a wired Cat-5 network cable. Plug it into the laptop and then into the router; reboot and test the ipconfig again.
If other workstations are on the network, do the same IPConfig test to see if they respond with a valid IP Address. If they have an address, the problem is with the workstation's network card, wiring or local software.
If IPConfig responds with a wrong address: 192.168.1.2 address when another address, such as 200.100, 101 was expected, then then the router has lost its configuration. Follow the steps in the configuration/setup article to re-program it (or restore your backup configuration). See this link: Setting up a Home Network DSL/Router
4. Bypass the Router for this test:
(This test only works with a wired connection and for this reason, I keep a short Cat-5 Network cable handy.)
If no IP Addresses can be found on your machine, or any other machine, unplug the network cable that leads from your PC to the Linksys/router and connect it directly into the DSL or Cable Modem (bypassing the Linksys). With a direct connection to the Modem, reboot the computer and check your IP Address again; it will be different than 192.168.1.100. If you do have an address, something is wrong with the router; it may need to be re-programmed, rebooted, etc.
If the direct-connection to the DSL or Cable Modem returns an IP Address, but the PC cannot browse the Internet, the problem is likely with the DSL/Cable Modem or with your ISP (assuming you trust the local PC's hardware and setup). Start looking at the blinky lights on the DSL/Modem. Consider calling your ISP and asking them to test the circuit (DSL). Leave the network in this state while working with the ISP, this way they can't blame your internal router.
If the direct-connection to the Modem does not return an IP Address (ipconfig), log-into the DSL/Modem and confirm DHCP is enabled. Confirm the local workstation is set to use DHCP (not detailed here.) Both of these ideas are not likely to happen as almost all equipment is set to use DHCP.
Testing the Linksys Router
Return the router to the network (wiring from Walljack to DSL/Cable Modem, to Router, to Workstation) and continue with these tests.
Reboot all workstations on the internal network. Assuming an IP Address is present on your workstation, consider Pinging other devices on the network. You can "ping" other workstations, network printers or the router itself. If any of these devices respond to the ping-test (below), your workstation and the router are configured correctly. Here are the details for the ping tests:
1. Assuming your workstation has a valid IP address: At the DOS prompt, 'ping' the router with a "dot.1" address. This address can vary, depending on how your network was built, but for most, use this address -- taking your workstation's returned IP Address and change the last octet to "1". Thus, if your workstation was given an IP Address of 192.168.200.1, ping 192.168.200.1:
ping 192.168.200.1
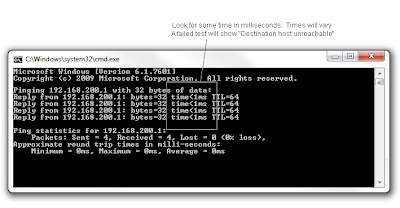
Decision:
If this test succeeds "time<1ms", then the Router is probably working correctly.
Continue with the DSL Modem test.
If this test fails "Destination host unreachable", check these possibilities:
a. Reboot the router by unplugging the power cable; wait 10 seconds, then plug back in.
After a minute, reboot your workstation and re-test with an IPConfig and Ping test.
b. If the Ping test still fails. Confirm the network cables are plugged in to your workstation and the router. If wireless, confirm the wireless card is active (Control Panel, Manage)
c. For wireless devices, switch to a wired connection and test again. If the wired connection succeeds, but the wireless fails, this is probably a software issue - either in the router or your workstation. More details on this, below.
Test the DSL Modem:
2. Test the DSL/Cable Modem.
If the workstation gets a valid IP Address (192.168.200.100, 101, etc.) and the Router Ping tests succeed, but you still cannot connect to the Internet, test the DSL Modem.
This assumes these addresses; your equipment may be different:
Workstation: 192.168.200.101 (or 192.168.100.101)
Router: 192.168.200.1 (or 192.168.100.1)
DSL/Modem: 192.168.0.1
ping 192.168.0.1 (Pinging the DSL/Cable Modem)
If the ping answers, suspect a problem with your workstation's firewall or virus protection software.
3. If 'ping 192.168.0.1' fails, do this test, if you did not already test this from above:
a. Plug your workstation (wired only) directly into the Ethernet port of the DSL Modem and reboot to get a new IPAddress range. (Temporarily unplugging the illustrated yellow connection between the Modem and the router.)
b. Do an "IPConfig"; expect an address similar to 192.168.0.2
c. Ping www.google.com (most web addresses will not respond to a ping, but google does). If google responds in 60 to 400ms, then the DSL modem is functioning properly and the problem is within your local network - it could be harware or software.
If you can ping google (while connected directly to the DSL) but cannot browse, suspect a software problem with the browser, firewall, virus software.
If you re-connect back to the Router (reboot to get a new IP Address) and you still can't browse, suspect a problem with the router. Perhaps the router has physically failed?
4. Can't PING Google while directly connected
If you can't Ping google, suspect a problem with the ISP/phone company. Call your DSL provider and ask them to check the line. It could be a problem with the hardware itself. If this device fails, it can be difficult to debug. The DSL/Cable modem may have "reset" itself to a new, default IP address. Your workstation's IPConfig test should give you a hint on where to test (ping .1)
Consider resetting the DSL/Cable Modem to factory defaults. Follow the DSL/Cable Modem's instructions or see my previous article for steps.
Related articles:
Setting up a Home Network DSL/Router
How to upgrade Linksys BIOS
Windows 7 and Vista Network Problems (IPV6)


No comments:
Post a Comment
Comments are moderated and published upon review. (As an aside, not a single spam has been allowed through; why bother?)