Manually setting up this router is relatively straight forward and simple and you will not need the router's CD. I recommend not installing the modem's setup program, saving you from a lot of junky software.
Setup takes less than 10 minutes and these are my recommended steps. Almost all DSL and Cable Modems follow similar steps. Use these instructions for new or re-configured routers.
Related article:
Keyliner: Linksys EA2700 Wireless Router - First Time Setup
Note: This modem is an ADSL modem and is likely obsolete. If your ISP supports "VDSL" modems, you should switch to a new modem. Contact your ISP to find out.
Note: Although these instructions will work with any DSL or Cable Modem, these instructions should only be used if the DSL Modem has only 1 (yellow) network port. If you have 1-4 yellow network ports, see this article instead: http://keyliner.blogspot.com/2017/09/zyxel-c1100z-dsl-modem-setup.html
Basic Setup
1. Obtain DSL Login credentials
You will need your DSL login account credentials from when the DSL line was first installed. This is not your computer's login or any other login that you would normally type and you may need to tunnel into your filing cabinets to find it. This will contain your DSL accounts user-id and password for the circuit. If misplaced, contact your ISP.
ATT 877.722.3755
Century Link / Qwest: 877.348.9005 or 888.777.9569
Verizon 800.567.6789
For other ISP's, please leave a comment so I can update this list.
2. Discover DSL Type
DSL comes in two incompatible flavors. A slightly older, but still commonly used in America, "ADSL," which is what this article describes, and a newer version is called "VDSL."
In general, ADSL is probably a safe assumption, and this article assumes you bought a Netgear ADSL modem. However, with this said, if your ISP supports VDSL, you should abandon this modem and get a more modern device. I know my circuit is ADSL, but a friend's house, 20 miles from mine turned out to be a VDSL and this modem would not work at that location; the two technologies are incompatible. This took several days to figure this out and was frustrating. See diagnostics at the end of this article.
3. Connect the DSL, as illustrated
Wiring:
- Connect a standard "silver satin" flat phone cable (RJ-11) from the wall-jack directly to the modem into the grey-port. Do not use a DSL filter on this line. On newer packaging, this is the "green" cable.
- If you also need a voice telephone on the same connection, use the RJ-11 Y-adapter that came with the router. If you are using a different brand router, you may need to buy a separate Y-adapter. With a voice-phone, place a DSL filter on the telephone-side. If your brand of modem has a second telephone jack built-in, a DSL filter is not needed.
- Temporarily connect an RJ-45 network cable directly to a PC or laptop hard-wired network connection using the cable provided with the modem (yellow port, often a yellow cable). You cannot use a wireless connection for this setup; it must be hard-wired.
- Install DSL Line filters on all other devices connected to the phone line. This includes all handsets, caller-ID boxes, answering machines, TIVO or recorders that are connected to the phone line. DSL filters were provided with the modem and you must do this prior to the next steps. If you used a Y-adapter on the modem's RJ-11 port, the phone on that half of the connection will need a filter.
4. Power-up the modem
a. Plug in the power-adapter
b. Press the black button (round, black button, back-side of router, illustrated above)
5. Boot the attached computer.
The computer will get a new IP Address.
6. Confirm LED status
Power (top icon) = Green
Ethernet (second icon) =Solid or blinking green
DSL (third icon) = Green
7. Start a browser session
From the PC, launch a browser and connect to this IP Address:
Connect to URL: 192.168.0.1
UserName: admin
Password: "password" no quotes
(* this is default, factory value, which will be changed in a moment)
7a. On launch, cancel the modem's firmware update check - because it won't work yet. It will be manually restarted later.
8. Configure Software settings:
In "Basic Settings," on the left-nav, make these changes:
a. set Encapsulation to its default setting. Likely PPPoE, per your DSL vendor's recommendation. This will be in the letter your ISP sent you when the account was first purchased.
b. Select (*) Yes on "Does your Internet Connection require a Login"
c. Type the DSL credentials recorded in step 1. The password is case-sensitive.
d. Check (*) Get IP Address Dynamically from ISP (typical)
e. Check (*) Enable NAT
f. Click Apply and Test.
In "ADSL Settings," accept the defaults, which are documented here:
Multiplexing Method = LLC-Based, VPI=0, VCI=32, DSL Mode=Auto(Multimode)
9. Change the router's default password
- Click left-nav "Set Password" and change the password from "password" to one of your choosing. I like to use "bratwurst sausage9"
- Write password and tape to side of the router or use checklist, below
- You may be prompted to re-authenticate
10. Allow an update to the BIOS.
Now that the DSL credentials are in place, allow the router to look for a Bios/Firmware update. As of 2012.09, this Netgear modem did not have an update, but it does not hurt to look. Follow these steps:
a. Close the browser session
b. Re-launch browser, re-connect to 192.168.0.1. Authenticate with your new credentials.
c. Allow Firmware check / update to run
If new firmware/bios is found, it will download to your local PC.
On left-nav "Router Upgrade," browse to this file and follow on-screen prompts to upgrade.
Periodically, once every 6 months to a year, check for firmware updates. You can update on a Wireless or wired network.
11. Record Keeping
It is embarrassing and painful to lose your router's configuration.
Write this information in a safe place because if the Internet is down, you can't exactly jump on the net to find your contact information. Don't wait to do this because you will forget.
ISP Name: ______________________________________________
ISP Technical Support Number: _____________________________
DSL Login Credentials: _____________ / Password _____________
DSL/ISP Account Number: _________________________________
(Often your home phone number. If no home phone, they will provide a separate account number)
Modem Model Number: ____________________________________
Modem IP Address: 192.168.0.1 ____________________________
Admin Login and Password: admin / _________________________
Downstream Wireless Router IP Address: _____________________
(Optional, if you have a separate Wireless router; see below)
This completes the initial setup. Confirm by browsing to any internet site.
Factory Reset: If the modem was previously working, but now is not, especially after a power failure, you may need to reset the modem to factory defaults. Using a paper-clip, press and hold the reset button (back side, pin-hole near the yellow RJ-45 jack. Hold for 10 seconds with the power on. Once reset, repeat the steps in this article.
Additional Devices
Except in the simplest case, you would not leave your PC connected directly to the DSL's Ethernet port. Instead, you would install a second (wireless) router into the DSL's ethernet and would then connect all other devices to the second router.
For related instructions on configuring a wireless router, see this Keyliner article:
Linksys EA2700 Router - First time setup.
Note: Your ISP does not care if you have one or twenty devices on your internal network.
12. Optional: Connect Wireless Router Summary:
a. Disconnect your PC from the router's RJ-45 network jack.
b. Connect a network cable between the Netgear DSL router to eithernet port on the wireless router (typically, a yellow-plug to a yellow plug).
c. Connect your PC to any port (1-4) on the (Linksys) wireless router.
d. Reboot the wireless router to get a new IP Address.
From a previous article, a typical network would look like this, where the Linksys Router (or other brand) is your wireless router. Illustrated, a different branded DSL router:
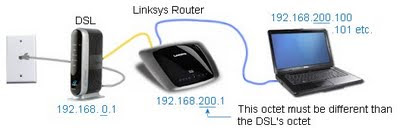
Consider putting your DSL and Wireless router on a small UPS. It will protect this equipment from being fried or losing their configuration during a power-failure. After having several devices fry, I expect this will save money and time.
Your DSL router setup is complete.
LED Status Details and Debugging:
The vendor's online documentation (which may not be helpful when you can't get on the internet) has a good debugging and diagnostics section at the back of the manual. See this link: NetGear Product Documentation. Below is a summary, showing normal and abnormal indicators.
Power LED
Solid Red -Modem is initializing
Solid Green - Power on (normal state)
If Red at other times, turn off the power, wait 1 minute, then power back on to see if the modem recovers. If this continues to fail, reset the modem to factory default (reset pin-hole button, see instructions above) and re-do the steps in this article.
Ethernet LED:
Solid Green - Devices connected (normal state)
Blinking Green - Devices active (normal state)
If Ethernet light is off, this indicates a problem with the yellow-cable connection. Confirm the downstream PC or wireless router is connected. Check the cable connections.
DSL LED [Icon looks like this: )00( ]
Off - No DSL signal
Solid Green - DSL signal (normal state)
Blinking Green - Initializing on power up.
If the DSL LED continues to blink, confirm the data-line to the DSL modem does not have a filter installed. If this still fails, disconnect all land-line phone devices in the house, including other phones, caller-ID boxes, answering machines, TIVO or Satellite boxes, home security systems. Reboot the router and test again. If the LED goes solid green, you are probably missing a DSL line filter on one of those devices.
If the DSL LED is off, confirm DSL line filters (see step immediately above). If you have multiple phone lines, confirm you connected to the correct circuit. It may be necessary to swap DSL signals on pins 1 and 4 on the RJ-11 jack. Contact your ISP for instructions. Be aware this DSL modem uses pins 2 and 3 for its signal.
If the DSL LED continues to be problematic, consider whether your curcuit is an ADSL (older, but common) or a newer VDSL. The two types are incompatible and an ADSL modem will not work on a VDSL circuit. You will have to contact your ISP to find out which you have.
Source: Wikipedia article 2012
If this does not resolve the problem, contact your ISP and ask them to test the line. This may also indicate a poor-quality or damaged line in your house.
Internet LED [Icon looks like ?i]
Off - No internet connection - likely an ISP problem or bad ISP password
Solid Green - Internet detected (normal state)
Blinking Green - Internet activity (normal state)
If the Internet LED is red, the device can see the DSL signal but cannot connect to the Internet. Verify your DSL Login credentials; the password is case-sensitive and usually contains upper-cased letters. Check with your ISP to see if the advanced settings "VPI and VCI" are set correctly, per their recommendations. This may indicate the ISP is having technical problems.
Finding your Router's IP Address
If you installed the router and later wanted to connect to its IP address (to update the BIOS, etc.), but you forgot to write down the address, it can be discovered with this test. This assumes you changed the default address from 192.168.0.1 to a different address:
a. Open a DOS Command Prompt.
b. Type this command, no quotes: "tracert www.google.com"
The first or second response will be your DSL router, depending if you are passing through a home wireless router or not.
DSLReports.com speed test:
Of interest, I am running on a 7mbs aDSL circuit (upgradeable to 12). DSLreports.com's line test shows these results in a late-night test from Boise, ID to LA,CA.
Speed Test #102812136 by dslreports.com
Run: 2012-09-27 23:56:18 EST
Download: 5830 (Kbps)
Upload: 698 (Kbps)
In kilobytes per second: 711.7 down 85.3 up
Tested by server: 55 java
User: 2 @ dslreports.com
User's DNS: qwest.net
Compared to the average of 78 tests from qwest.net:
* download is 36% better, upload is 32% worse
Subsequent tests on 2016-09-07 - with the same DSL Modem this article was written with, on the same 7mbs circuit, here are the latest from dslreports:
Download: 6050 (kbps) 6.05 (mbs)
Upload: 7552 (kbps)
Overall Speed Rating "C"
Quality: "D"

Qwest / Century Link has their own DSL speed test, found here: Qwest DSL Speed Test
with these results:
File size transferred : 1.04 MB (1090681 bytes)
Total time taken : 1.74 seconds (1739 milliseconds)
Throughput : 627.0 KB/sec [Kilobyte-per-second]
= 0.63 MB/sec [Megabyte-per-second]
= 5016.0 Kbps [Kilobit-per-second]
= 5.02 Mbps [Megabit-per-second]
Neither are scientific tests and are subject to latency and other variable delays. No circuit will reach its rated throughput -- in other words, I would never expect 7mbs, getting 5.8 is close enough.
Author's note: Since this article was written, the author upgraded to a VDSL modem, and bumped up to a 20mb circuit. Speedtests now show about 15mb/s See the Zycell article, below.
Related articles:
Zycel C1100z DSL Modem Setup
Linksys EA2700 Wireless Router review
Linksys EA2700 Wireless Router - First time setup / setting up a home network
Windows 7 Unidentified Network problem
Installing an upgraded laptop wireless card
Wireless printer fails after router upgrade





No comments:
Post a Comment
Comments are moderated and published upon review. (As an aside, not a single spam has been allowed through; why bother?)