DirectoryPulse - keyliner Backup Software
-2025.11 - Version 2.30 - Added second local drive support: "L2"
Fixed minor bug in Cloud Default cursor-focus
Fixed "none" option in system config
Backup large swaths of directories to a separate drive. Files can be saved in dated folders, as compressed files, or as generational backups (multiple versions of files). Jobs can be saved and re-loaded, and scheduled for automatic runs.
Backup are non-proprietary and fast!
Write to local drives, SAN drives, and cloud drives, organized by project, by date, etc.
 |
| (Click for larger view) |
Features:
* Backup to a local disk, SAN, One-drive, GDrive, etc.
* Non-proprietary backup - straight-forward file-copies
* Backup to optional dated-folders (YYYY-MMDD)
* Supports Generational backups
(multiple versions of same file, V1, V2, etc.)
* Optional ZIP backups
(reduce upload times to OneDrive)
* Can skip non-changed files
Automatically skip cache folders, temp files, and hibernation files
Automatically skips Windows System Files
Skips One-drive virtual file links (saving re-downloading)
* Manages its own backup inventory, erasing old backups
* Configurations can be saved for easy retrieve and re-run
* Automate and schedule with Windows Scheduler
* Occupies zero RAM or resources when not in use; no background tasks
* Includes a nifty Directory Report that displays a sortable report, showing file-sizes and counts in a way that file explorer does not. Use this to find your biggest disk hogs.
DirectoryPulse was originally written as a Student and Instructor exercise in Volume 6 of the Computer Programming Book, War and Peace Programming in C# -- Amazon Kindle, written and published by keyliner. It grew into this program.
Try it:
See below for download and installation instructions.
1. Launch program, "DirectoryPulse.exe" from the Start Menu tile or by double-clicking the .exe.
The program was written with C#, .DotNet 8.0. When first launched, you may be prompted to install Microsoft's .DotNet 8.0 libraries.
2. On first-launch, you are prompted for default backup destinations. These are one-time settings.
Most users setup these destinations:
D:\drive (local secondary drive, or USB disk)
SAN (local network disk, or assign to a USB disk)
Cloud (Onedrive or GDrive backup folder)
For each destination, type or browse to a top-level "backup" folder name -- such as "Backups"; all backups, of any type, will live in this folder. (Optionally, browse to each destination. Use the word "none" to disable the SAN or CLOUD destinations.)
 |
| Click for larger view |
Save the changes and return to the main panel.
The program builds the top-level destination directory automatically when you close the panel.
3. On the main panel, select which directories to backup.
In the top-most field, type the path, browse, or use File Explorer to drag-n-drop a folder onto the target.
(DirectoryPulse! only cares about folder-backups; you cannot select an individual file.)
Optionally, right-mouse-click the field and choose "Add User Profile Documents".
+Multiple folders can be stacked into the backup job.
4. Click Button "Refresh DOS Directory List"
This inventories the folders and shows a nifty report, showing all directories and subdirectories, with file counts and sizes. Sort by column-headings; right-mouse-click for a context menu. This list is used by the backup.
5. Session Settings:
Set a backup destination and other preferences by clicking the Gear icon:
Click the "Gear" icon (-- this job's configuration settings)
Name this configuration file (e.g. "MyFavoriteBackup" or "Local-DataFolder")
Type a short description
Choose the type of backup ("Dated Folder [1-10]" - recommended)
 |
| Click for larger view |
Set a pre-named sub-folder (which helps to build-out a destination-path). Subfolders, such as "Projects", "Monthly", "Adhoc" are offered.
Choose Adhoc or (None) if you have no opinion. I typically use "Projects" (aka all my project backups go to the Project folder)
Once the subfolder is selected, a suggested backup destination path is constructed. This is an assembled path, but can be changed manually to any other path (destination). Destination folders are built automatically when the backup starts.
The default subfolder names and other paths are adjustable. See "System Defaults", this panel.
See the next article for Detailed Switch documentation.
6. "Save" these preferences or click "Apply" to only use for this session.
7. From the main screen, click bottom-row button "Backup"
The backup runs. The backup re-creates the source-path (backup folders) in the destination path, creating each directory, one-for-one. For example, if backing-up C:\data\subfolder1, the backup destination might be D:\Backups\adhoc\data\subfolder1.
When done, a report displays, along with a log file.
If the backup type is "Dated Folder [1-10]", the backup destination has a subfolder:
For example: D:\Backups\Adhoc\2024.0804. In this folder is a duplicate of the source drive's directory structure, with all eligible files.
Each time this configuration is run, it creates a new folder, keeping 10 generations of backups. On the 11th backup (the 11th date), the oldest date is automatically deleted -- a self-cleaning backup.
Details and additional program documentation can be found here:
Detailed Switch documentation
Installation Steps:
DirectoryPulse is free to download and use for personal and commercial use.
No registration, no login, no email. No advertisements, no nags, no spying.
Keyliner does not (and cannot) track who downloads or runs this program.
Installation is easy:
Download the .exe (.zip) and copy its supporting files into any folder on your hard disk.
Double-click the .exe to run - no installation required.
Using the .exe from a download folder, or copying to a (my Documents) folder is a quick workaround for various Windows security concerns. Some vendors recommend this, but these folders are inappropriate for executable software. Instead, the program should be copied to Program Files so it gains the protection of other Windows security features. Total time: about a minute.
Follow these steps for a more professional installation:
From Keyliner's public GDrive, click this link and download to a local temp or download directory.
Version 2.30 Download Link
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1ah3ulKgRWmU48YYckkzC9-Mb29Pciesc?usp=drive_link
When downloading, different browsers behave differently.
Select "Save-As"
Windows security will not let you download directly into Program Files -- you must save to a temp directory (technically, you will not be able to remove the "mark of the web" if downloaded directly into Program Files).
Since keyliner cannot afford a signing certificate, you will be prompted that the file is not safe (being downloaded from the internet). Click "more information" and allow the program to download/run.
Zip File Hashes:
MD5: 93-65-81-b2-de-d9-cc-9c-09-d1-64-4a-40-d9-79-5d
SHA256: 8465cb911b37d2b80f2f76dff0d714f4fd0488a2add739281cc2790c3d529f9e
B. Mark the download as safe-to-run:
Using File Explorer,
Right-mouse-click the downloaded DirectoryPulse.zip
Select "Properties"
Check [x] Unblock. (This removes the "mark of the web.")
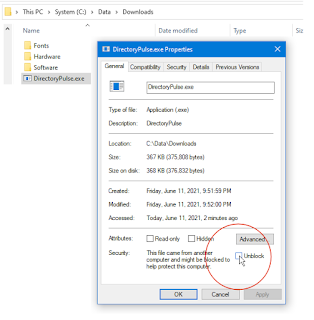 |
| Click for larger view |
* Only do this if you trust
keyliner *and* only if downloaded from keyliner's public GDrive.
If
"Unblock" is not visible, it has already been unlocked (by Microsoft
Edge).
Once [x] Unblocked is clicked, this security menu disappears.
C. Create a Program folder to hold the program:
Using File Explorer, open folder C:\Program Files,
Create a new utility folder: C:\Program Files\Util
D. Copy the .exe and two support files to ProgramFiles\Util:
Using File Explorer,
Double-click to open the .zip folder
Copy/paste three files from the zip,
Paste to C:\Program Files\Util
DirectoryPulse.exe
DirectoryPulse.dll
DirectoryPulse.runtimeconfig.json
Do this copy as a two-step,
copying from the temp/download folder, then into Program Files.
E. Create a Start Menu Tile:
Tunnel to C:\Program Files\Util
Right-mouse-click the DirectoryPulse.exe and "Pin to Start"
The program is ready to run. See icon on Start Menu.
On first-time launch, you are prompted for default backup destinations -- choose where to write backup files. See details earlier in this article, with additional program documentation here: Detailed Switch documentation
Version history:
2.30 - 2025.1123 Added support for second local drive (drive E:); "L2"
Fixed cursor positioning problem when setting Cloud Default paths
Improved (fixed) "none" support for non-Local (L1) destinations
Improved a minor mouse-over tool-tip message in System Settings
Changed how job options behave when the backup type is changed
2.20 - 2025.0707 Added Filtering to the Pref File Load panel
2.02 - 2024.1005 Still had problems with high-resolution laptop screens; believe now fixed
2.01 - 2024.0923 Fixed display problem on laptops with high-resolution screens (140%)
2.00 - 2024.0810 Numerous design changes.
Improved Configuration selection and prompts
Simplified Backup-type and option settings
Added subfolder-cosmetic tagging
Added drag-n-drop support
Added eyecandy to help guide decisions
Improved backend INI file settings
Note: Version 1.x INI config files not compatible with this version; sorry. You will have to rebuild the config files.
1.05 - 2023.0430 Moved the Config/INI lookup button to top of panel
Added cosmetic "Destination:" during the backup
Added a "Delete" button (in addition to the Context menu) for INI Delete
1.04 - Fixed bug where sometimes root drive not inventorying: "Unexpected error in DOS directory"
1.03 - Minor changes to the report Log file, making it easier to find skipped directories
1.02 - Not released
1.01 2021.0610 Initial Release
Thank you to my Beta-testers: DLW, of Boise.









